Dogs are known for being carnivorous animals, so it may come as no surprise that they can eat meat. In fact, many dog foods are made with meat as the primary ingredient. However, not all types of meat are safe for dogs to consume, and it’s important for pet owners to be aware of what their furry friends can and cannot eat.
In this article, we will delve into the advantages and possible concerns of including meat in dogs’ diets, pinpoint safe and appropriate meats for dogs, comprehend the proper method of introducing meat into their diet, and recognize the significance of moderation.
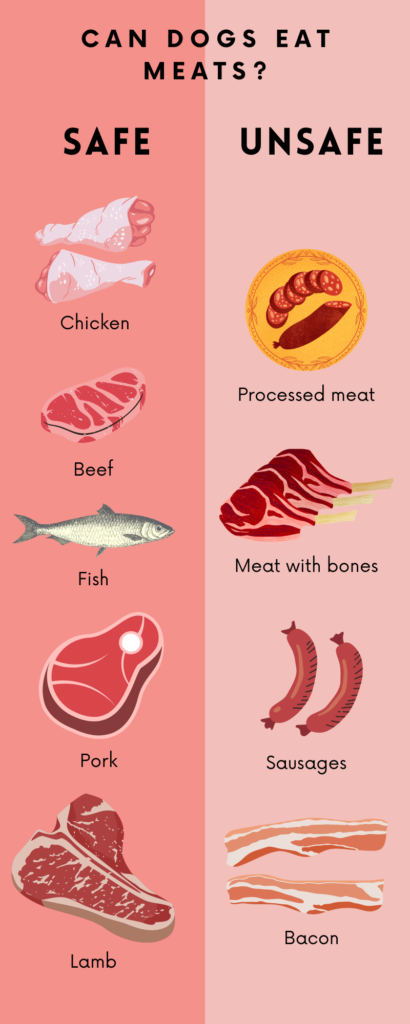
Can Dogs Eat Meat?
Yes, dogs can eat meat. Meats are a great source of energy and are essential for maintaining a dog’s muscle mass. They contain proteins, fats, and other vitamins and minerals that are very beneficial for the dogs. They are one of many other foods that can be safely shared with your dogs.
While dogs can technically eat any type of meat, it’s important to note that some meats are healthier for them than others. Lean meats, such as chicken and turkey, are great sources of protein for dogs and can be easily digested.
On the other hand, fatty meats like bacon and sausage can cause digestive issues and even pancreatitis in dogs if consumed in large quantities. Additionally, some types of meat, such as pork and beef, may contain harmful bacteria like salmonella and E. coli, which can make dogs sick if not cooked properly.
Nutritional Needs of Dogs
Dogs are primarily carnivorous animals and require a diet that is rich in animal protein. They have specific nutritional needs that must be met in order to maintain their health and wellbeing. Here are some of the key nutrients that dogs require in their diet:
Protein
Protein is an essential nutrient for dogs, as it provides the building blocks for their muscles, skin, and other tissues. Dogs require a higher amount of protein than humans do, and it should make up a significant portion of their diet. Good sources of protein for dogs include meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
Fat
Fat is another important nutrient for dogs, as it provides them with energy and helps to keep their skin and coat healthy. Dogs require a higher amount of fat than humans do, and it should make up a significant portion of their diet. Good sources of fat for dogs include meat, fish, and oils such as fish oil and flaxseed oil.
Carbohydrates
While dogs do not require carbohydrates in their diet, they can be a good source of energy and fiber. However, it is important to choose high-quality carbohydrates that are easy for dogs to digest, such as sweet potatoes, brown rice, and oats.
Vitamins and Minerals
Dogs require a variety of vitamins and minerals in their diet in order to maintain their health. Some of the most important vitamins and minerals for dogs include:
- Vitamin A: Important for vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and immune function.
- Vitamin E: Important for skin health and immune function.
- Calcium: Important for bone health.
- Phosphorus: Important for bone health and energy metabolism.
- Iron: Important for oxygen transport in the blood.
Dogs require a diet that is rich in animal protein, fat, and essential vitamins and minerals in order to maintain their health and well-being. It is important to choose high-quality ingredients and to provide a balanced diet that meets their specific nutritional needs.
Benefits of Meat in a Dog’s Diet
Meat is a primary source of protein in a dog’s diet and provides numerous benefits to their overall health. Here are a few reasons why including meat in a dog’s diet is essential:
Protein
Protein is essential for a dog’s growth, development, and maintenance of muscles, tissues, and organs. Meat is a rich source of protein and contains all the essential amino acids that a dog’s body needs. It aids in the repair of tissues, helps to regulate hormones and enzymes, and supports the immune system.
Nutrients
Meat contains essential nutrients that are vital for a dog’s health, such as iron, zinc, and B vitamins. Iron is crucial for the formation of red blood cells, while zinc helps to maintain healthy skin and coat. B vitamins play a vital role in energy metabolism and help to keep the nervous system functioning correctly.
Palatability
Dogs are natural carnivores, and meat is a highly palatable food for them. Including meat in their diet can encourage them to eat and maintain a healthy appetite. It can also make mealtime more enjoyable for them.
Variety
Meat provides a variety of flavors and textures that can add interest to a dog’s diet. Including different types of meat can help to prevent boredom and ensure that a dog is getting a balanced diet.
Overall, meat is an essential component of a dog’s diet. It provides protein, essential nutrients, and palatability, and can add variety to their meals.
Introducing Meat to Dogs
Adding meat to your dog’s diet can be a healthy and flavorful addition to their meals. However, a gradual and mindful approach is essential to ensure a smooth transition and your furry friend’s well-being. You can follow the following steps to safely introduce meat to your beloved canine companion:
- Start with Lean, Cooked Meats:
- Opt for lean meats like chicken or turkey, as they are less likely to upset your dog’s stomach.
- Cook the meat thoroughly to eliminate any potential bacteria and to make it easier for digestion.
- Mix Meat with Regular Food:
- Begin the introduction by mixing a small amount of cooked meat into your dog’s regular food.
- Use a 75% regular food to 25% meat ratio initially to allow them to get accustomed to the new taste.
- Observe for Reactions:
- Monitor your dog closely for any signs of allergies or digestive discomfort after introducing the meat.
- Look for symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive itching, which may indicate an adverse reaction.
- Gradually Increase Meat Portion:
- Over the course of several days, gradually increase the meat portion while decreasing their regular food.
- Aim to reach a 50% regular food to 50% meat ratio by the end of the transition period.
- Monitor Digestive Health:
- Keep a close eye on your dog’s stools during the transition process.
- If you notice any sudden changes in their bowel movements, slow down the introduction or revert to their previous diet.
- Consult Your Veterinarian:
- If you have any concerns or if your dog experiences persistent discomfort during the transition, consult your veterinarian.
- Your vet can offer personalized advice and ensure your dog’s specific dietary needs are met.
By following this guide, you can ensure a smooth transition and provide your furry friends with a nutritious and delicious addition to their meals.
Remember, each dog is unique, and what works for one may not suit another, so always be attentive to your pet’s individual needs and preferences.
Potential Risks of Feeding Dogs Meat
While dogs are known to be carnivorous animals, feeding them meat comes with potential risks that owners should be aware of. Here are some of the risks associated with feeding dogs meat:
Raw meat
Feeding dogs raw meat can expose them to harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli, which can cause serious health problems. These bacteria can also be transmitted to humans through contact with the dog’s feces or saliva.
Bones
Bones can cause several problems for dogs, including choking, intestinal blockage, and tooth fractures. Cooked bones are particularly dangerous as they can splinter and cause internal injuries.
High Fat Content
Meat is generally high in fat, which can lead to obesity and other health problems in dogs. Excessive fat intake can also cause pancreatitis, a condition that can be life-threatening.
Allergic Reactions
Some dogs may be allergic to certain types of meat, which can cause skin irritation, itching, and digestive problems. It is important to monitor your dog’s reaction to new types of meat and consult with a veterinarian if you notice any adverse effects.
Nutritional Imbalance
Feeding dogs only meat can lead to nutritional imbalances as meat does not provide all the necessary nutrients that dogs need. A balanced diet should include a variety of protein sources, carbohydrates, and vegetables.
Alternative to Meat for Dogs
Dogs have diverse dietary needs, and while meat is a significant protein source for them, there are plenty of alternative options that can provide essential nutrients. Here are some alternative food sources for dogs:
Vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli and spinach are not only packed with essential vitamins and minerals but also provide a healthy dose of antioxidants, contributing to your furry friend’s overall well-being. Just ensure to cook or steam them to make digestion easier for your dog.
Enhance your pup’s health with dog-friendly veggies. Check out this article on incorporating vegetables into their diet.
Grains
Whole grains such as barley and bulgur can be a fantastic alternative to meat, offering a good source of complex carbohydrates and fiber. These grains can aid in digestion and provide sustained energy for your active canine companion.
Discover the power of whole grains for your active pup. Learn more in this article dedicated to grains for dogs.
Nuts
While not all nuts are safe for dogs, cashews and hazelnuts, when given in small quantities and unsalted, can be a delightful treat for your pup. These nuts contain healthy fats that contribute to a shiny coat and healthy skin.
Delight your dog with safe and healthy nut treats. Find out which nuts are suitable in this helpful article on nuts and dogs.
Fish
Fish like trout and herring provide a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, supporting joint health and cognitive function in dogs. Adding a small portion of fish to your dog’s diet can be a tasty and nutritious addition to their mealtime.
Dive into safe seafood treats for your playful pup. Find out which seafoods are suitable in this helpful article on seafoods and dogs.
Fruits
Treat your dog to a refreshing snack of watermelon or raspberries, as these fruits contain natural sugars and valuable vitamins like vitamin C. Just be mindful of the portion sizes, as moderation is key when it comes to fruit consumption for dogs.
Treat your furry friend to refreshing and nutritious snacks. Explore fruits for dogs in this informative article.
Dairy
Adding a dollop of plain Greek yogurt or a sprinkle of low-fat cheese can be a source of calcium and probiotics, promoting a healthy digestive system in your canine companion. Remember to introduce dairy slowly and watch for any signs of intolerance.
Always observe your dog’s reaction to any new food and introduce them gradually into their diet to ensure a smooth transition and optimal health benefits. Consulting with your veterinarian will provide tailored guidance on the best alternative food sources for your unique four-legged friend.
Alternatively, here are other foods and fruits including the some miscellaneous foods that you can safely give to your dogs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while meat can be a valuable source of protein for dogs, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with feeding them meat. There are also alternative protein sources that can be included in their diet. Plant-based proteins, insects, and fish are all good options for dogs with allergies or sensitivities to meat.
Owners should consult with a veterinarian to ensure that their dog’s diet is balanced and meets their nutritional needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Dogs Eat Every Meat?
Whilst dogs can eat meat depending upon the age and health of the dogs, it might be not be suitable for dogs to eat every meat
What Is the Healthiest Meat for Dogs?
Chicken is one of the healthiest meat for dogs as it is high in protein and low in fat.
Can Dogs Eat Meat Everyday?
Yes, dogs can eat meat everyday but make sure they are not over feed.
Can Dogs Eat Meat Fat?
Yes, dogs can eat meat fat. However, it is recommended they are fed only in moderation
